How Blockchain is Revolutionizing the Payment and Banking Sectors
Payment institutions and their consumers have long been concerned about digital security. Payments must be simple, fast, and secure to improve and popularize digital payments. The most basic requirement is for the price to be transparent and quick. Software testing in financial services helps improve the services, making them more customer-focused.
Blockchain technology has developed a system that tackles payment security concerns, increases transaction transparency, and improves the overall efficiency of financial operations. The system operates without intermediaries, eliminating the requirement for a central regulator.
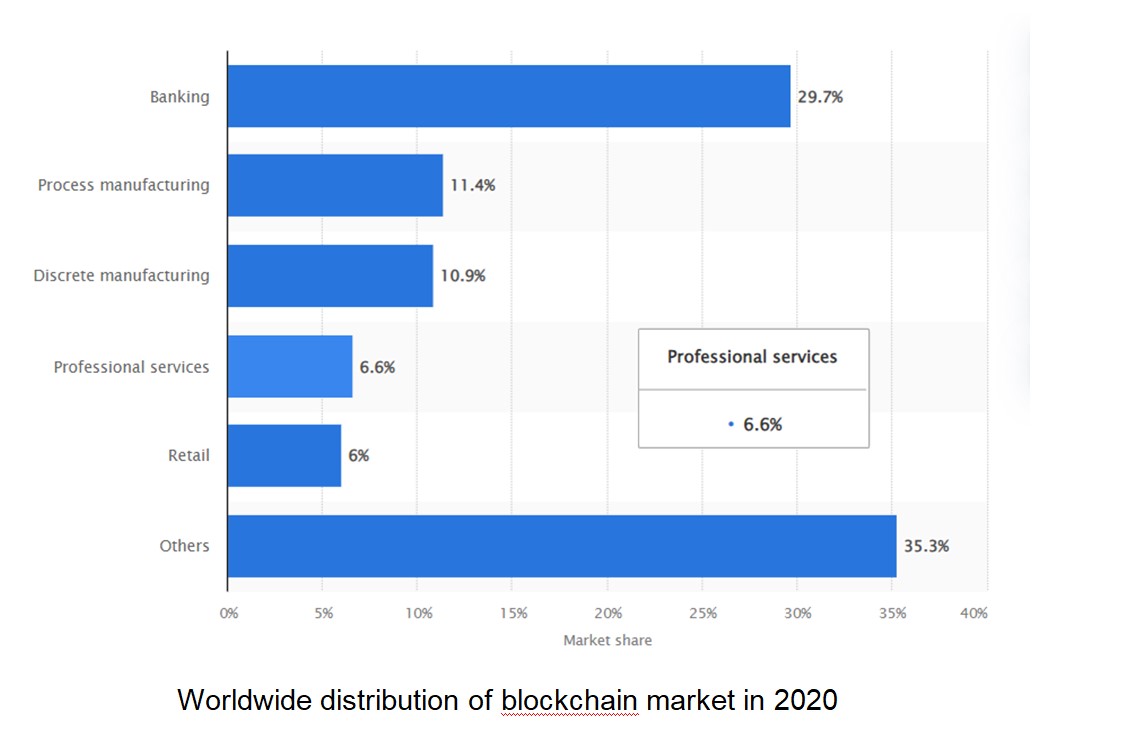
Worldwide distribution of blockchain market in 2020
.
What IS BLOCKCHAIN?
A distributed database or ledger shared across computer network nodes is called a blockchain. A blockchain is like a database. It saves information electronically in digital format. The blockchain is unique in that it maintains the correctness and security of the recorded data. It also generates confidence in the user without the need for a trusted third party. Blockchains have a critical function in cryptocurrency systems like Bitcoin, where they keep a secure and decentralized record of transactions.
The organization of data differs significantly between a traditional database and a blockchain. A database typically organizes its data into tables, but a blockchain, as the name suggests, collects its data into chunks (blocks) that are linked together. A blockchain accumulates information in groupings known as blocks, which store the data. When a block’s storage capacity is reached, it is closed and connected to the previous block, producing a data chain known as the blockchain.
Working of a BlockChain:
A blockchain is a foundation for immutable ledgers or records of transactions that cannot be erased, changed, or destroyed. Blockchain’s purpose is to enable digital information to be recorded and spread across the chain, but it cannot be altered. Blockchains are also called distributed ledger technologies (DLT) for this reason.
CROSS BORDER TRANSACTION:
Cross-border payments are financial transactions in which the payer and receiver are located in different countries. They include both wholesale and retail payments, as well as remittances. Cross-border payments can be made in a variety of ways.
In cross-border payments, blockchain technology can enable safe transfers across bank ledgers. It allows one to avoid financial intermediaries, who act as middlemen to facilitate money transfers from one bank to another. While blockchain technology has been employed in various sectors since its launch in 2009, it is still most commonly used in money transfers and transaction reconciliation. However, cryptocurrencies are not the only types of cash moved via a distributed ledger.
Challenges of Cross-Border Transaction:
Transaction Time:
A cross-border transaction typically takes three to five business days to complete. A considerable time zone difference between the two currency jurisdictions is critical. Money must be sent via the applicable domestic payment systems, and the operation hours of these domestic payment systems may differ across international time zones, delaying transaction settlement to settle each currency leg.
Transaction Fee:
Sending an overseas payment using normal banking channels is a complicated, multi-step procedure involving multiple intermediaries. Cross-border payments become costly since banks sometimes do not have direct contact with one another. In turn, they have intermediate banks to facilitate indirect financial transfers. The cost for this service is deducted, by the central bank, from the total transfer amount. This fee is borne by the sender and the recipient (or either side must pay the whole sum). This cost is a surcharge over any fees paid by the remitter or receiver bank. The price for a large volume of cross-border transfers is typically 2% to 3%. However, if payment volumes and values are low, they might rise to 10%.
Transaction Safety:
Different jurisdictions have varying regulatory standards, which adds risk to a transaction. Users’ data might be jeopardized if that authority is hacked, corrupted, or taken down. Furthermore, when records are retained by each central authority involved in the transaction, such as a bank, they are open to manipulation.
Transaction Opacity:
The ultimate payment amount and delivery date are both undetermined. Because there are several participants in a single transaction, tracking the money while it is in route is difficult. It is also difficult to trace vulnerable transactions rapidly. This is owing to the lack of an end-to-end system or rule set and the necessity to deal with many currencies across multiple time zones and meet various regulatory requirements.
Correspondent banking:
The number of correspondent banking connections is decreasing, particularly in areas where transaction volumes do not justify the bank’s compliance expenses and in jurisdictions where transactions may be high risk or compliance is challenging to achieve.
Liquidity:
Businesses and financial institutions may have various issues, with funds languishing in Nostro or Vostro transactional accounts worldwide, locking up cash that could be put to better use.
RECURRING PROBLEMS AND HOW BLOCKCHAIN SOLVES THEM:
Software testing for banking services is necessary to mend the issues faced by the users. Blockchain is one such example. Here we will discuss how blockchain helps to address the problems mentioned above.
Transaction Speed:
Blockchain payments are executed almost instantly – in seconds rather than days. The ability to immediately transfer money allows firms to be more responsive, acting on or addressing client requirements without waiting for the cash to arrive.
Transaction Fees:
By eliminating the mediators, transaction fees for transferring cross-border payments are reduced. Fees paid by transacting parties are confined to charges imposed by the operator of the distributed ledger technology-based service. Companies that use blockchain must only pay a modest amount, which is nearly nothing.
Transaction Security:
In blockchain technology, all transaction records are cryptographically protected, linked to prior transactions, and disseminated among participants through a ledger. Participants (buyers, sellers, and peers) establish channel-based private and closed communication to approve, validate, and commit transactions.
Network users use their private keys to sign transactions, a digital signature. If a record is changed, the digital signature is rendered invalid. As a consequence, the peers recognize that something has happened. Because blockchain is decentralized and runs on a peer-to-peer network, the ledger is constantly updated and synched among the members.
It means that the catalog has no single point of failure and that altering its state is nearly impossible. Changing the data recorded on the blockchain requires authorization from up to 51% of the members (all at once). Furthermore, compromising the network necessitates massive computational power. A hacker has to change all previous transactions in the ledger to tamper with the data.
Transparency and visibility of transactions:
While a user’s identity remains hidden in a public blockchain system, the transactions of each address are visible. Individuals, auditors, and regulatory bodies can examine all transactions carried out at that address using an explorer and a public lecture.
In contrast, the specifics of a transaction are only visible to authorized participants in a private blockchain system. On the network, all business logic is written as smart contracts. Because all acknowledgments are compiled and saved as events, the transaction is completely transparent and visible.
Data Integrity:
Blockchain eliminates the possibility of inconsistencies in record keeping. As a decentralized ledger, it keeps a verifiable and irreversible record of every transaction and makes it available to all authorized users. A collection of linked computers maintains and updates the ledger collectively, and all participants have an identical copy of the catalog.
Encourages competition and innovation:
As blockchain technology and blockchain-based payment enterprises have emerged, incumbent cross-border payment institutions have come under pressure. This healthy rivalry will spur innovation, which will benefit consumers.
Immunity to censorship by a central governing body:
There is no robust control of a central governing authority in peer-to-peer blockchain architecture, which is helpful for such worldwide transactions. Furthermore, virtual currency wallets cannot yet be emptied or blocked by banks or governments.
CONCLUSION
Financial services contain compromising data, no matter how we think about it. Payment methods must be fast and smooth and give users full rights and security over their data. That is why software testing in financial services is necessary.
Payment transactions require trust and transparency, which blockchain provides. Global investment in blockchain is predicted to reach 6.6 billion USD by 2021. According to forecasts, expenditures on blockchain solutions are expected to rise in the next few years, touching about 19 billion US dollars by 2024.
Enterprises that want to implement blockchain face privacy and security issues, anxiety about the blockchain integration process, integration problems with legacy systems, high energy consumption, and initial investments.